قدم تلسكوب “غايا” الفضائي، الاثنين، بياناته الجديدة حول ما يقرب من ملياري نجم في مجرة درب التبانة، بدقة مذهلة تجعل من الممكن رسم خريطة لمجرة تضج بالحياة.
وقال مدير عام وكالة الفضاء الأوروبية يوزف أشباكر، خلال تقديم نتائج تلسكوب “غايا” إحدى أبرز المهمات التي أطلقتها الوكالة سنة 2013: “إنه يوم رائع لعلم الفلك، ويفتح الباب على مصراعيه لاكتشافات جديدة حول الكون ومجرتنا”.
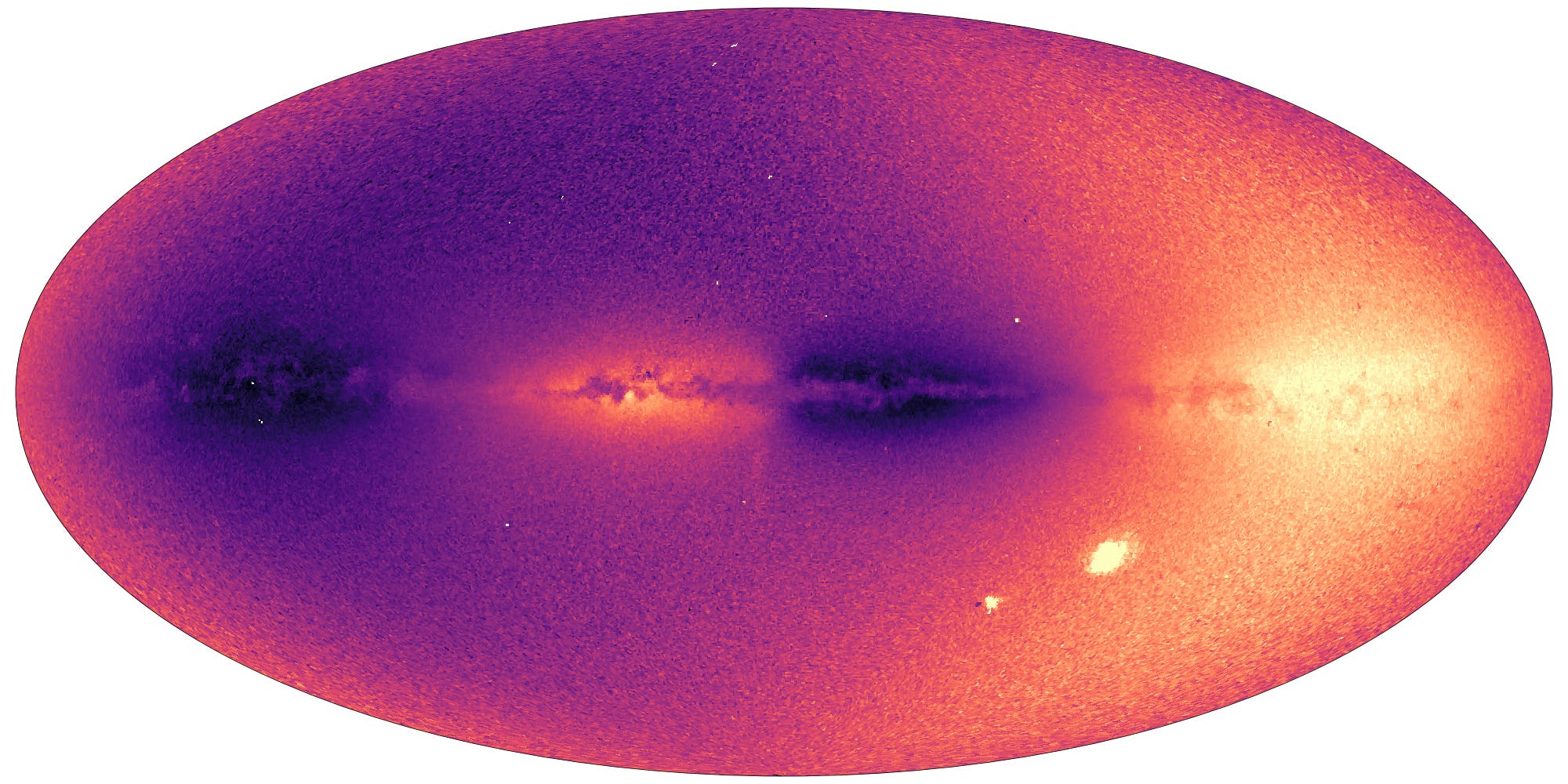
وهذه ثالث مهمة لجمع البيانات يقوم بها المرصد الفضائي المتمركز على بعد 1.5 مليون كيلومتر من الأرض مقابل الشمس، وتهدف إلى رسم خريطة لمجرتنا بجميع أبعادها، وبالتالي فهم أصلها وهيكلها ودينامياتها.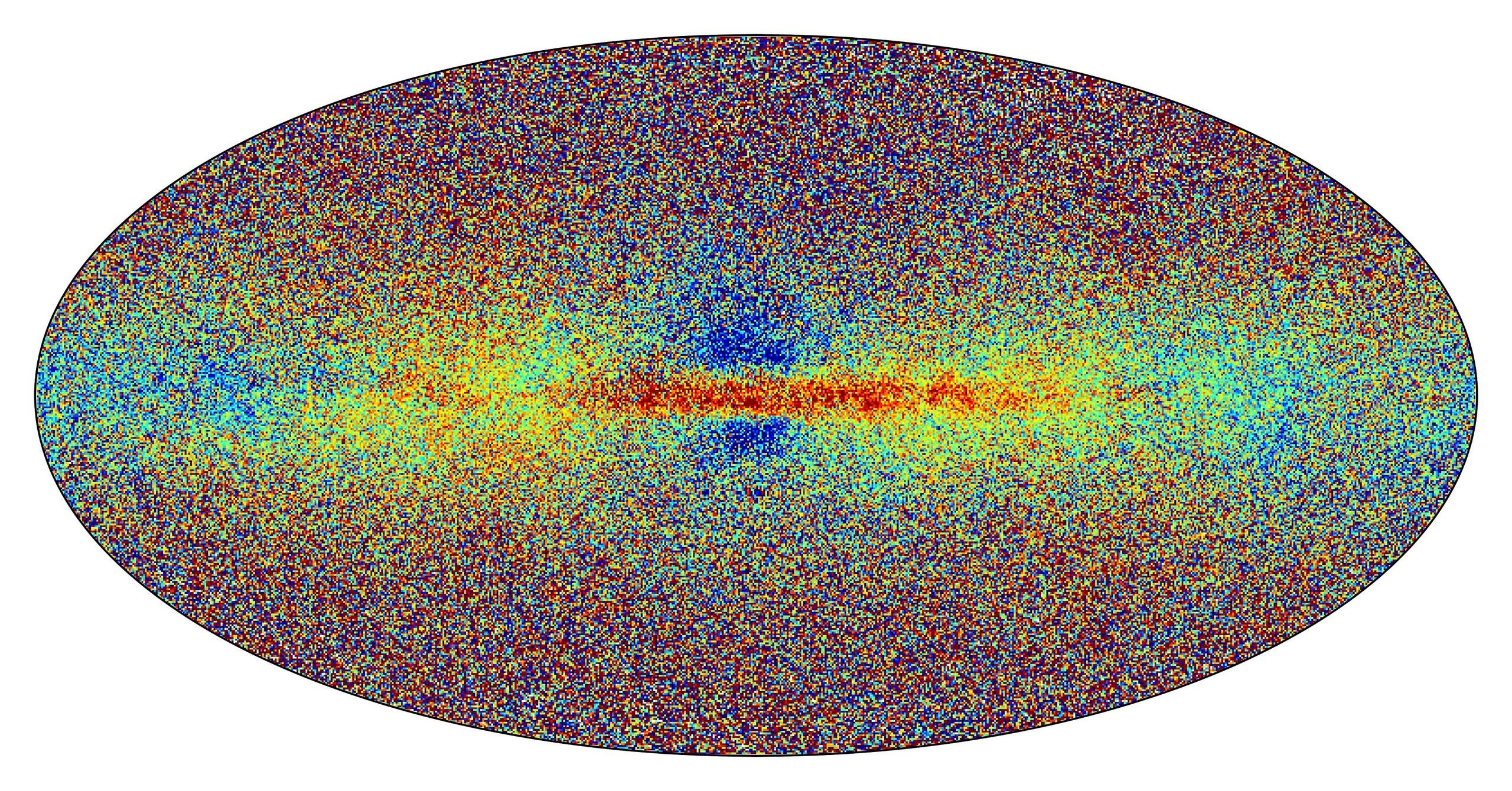
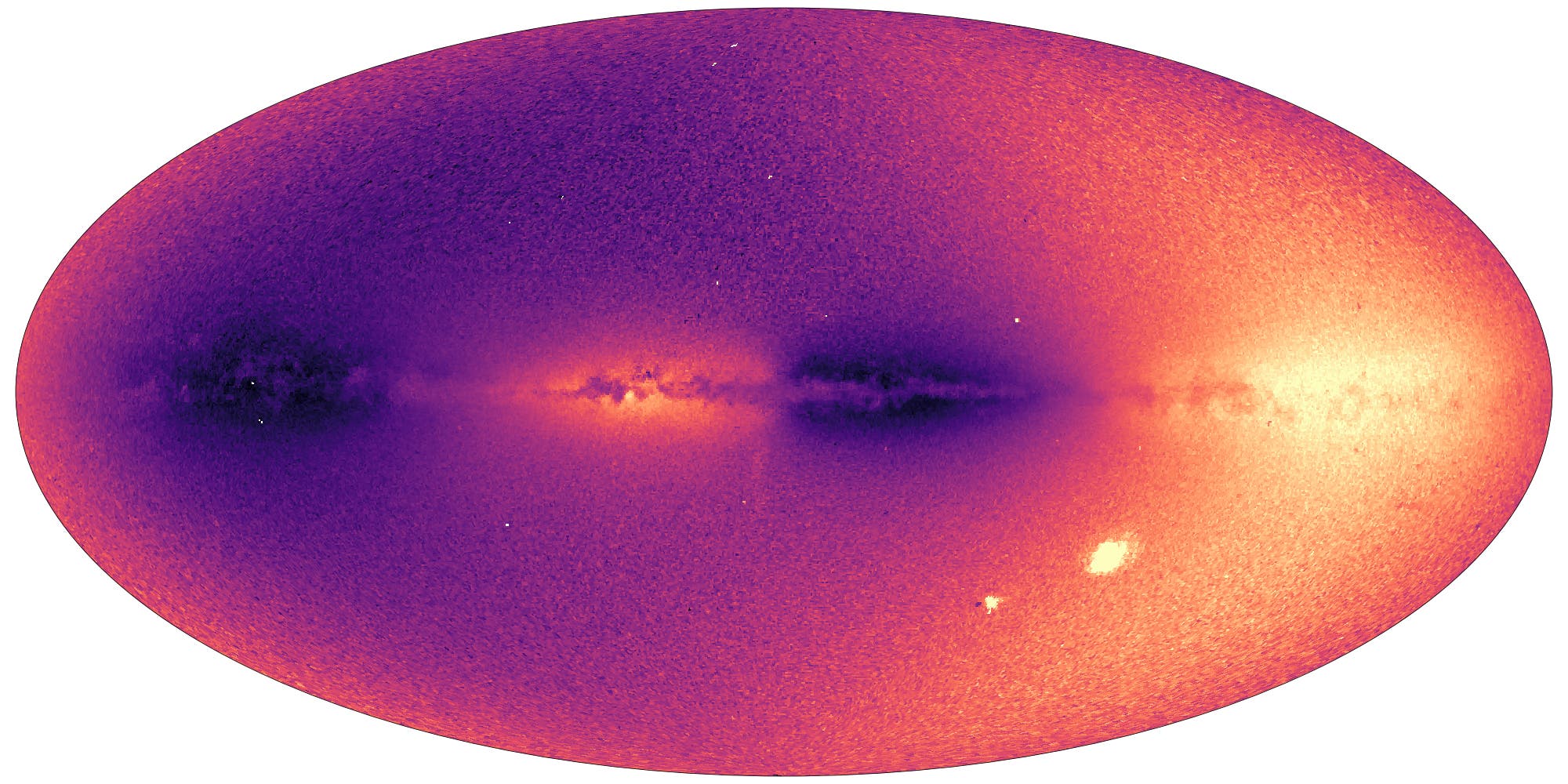
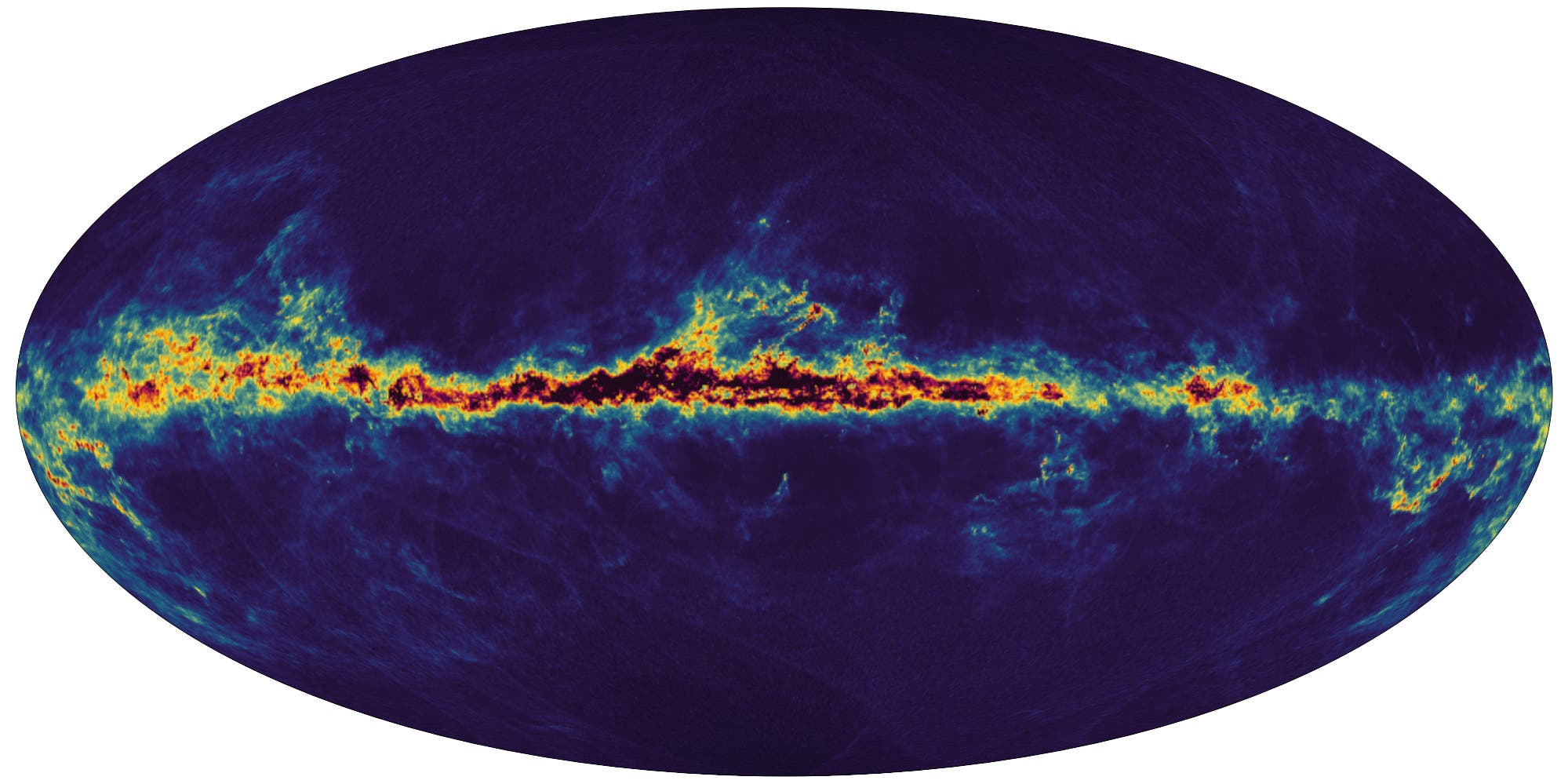
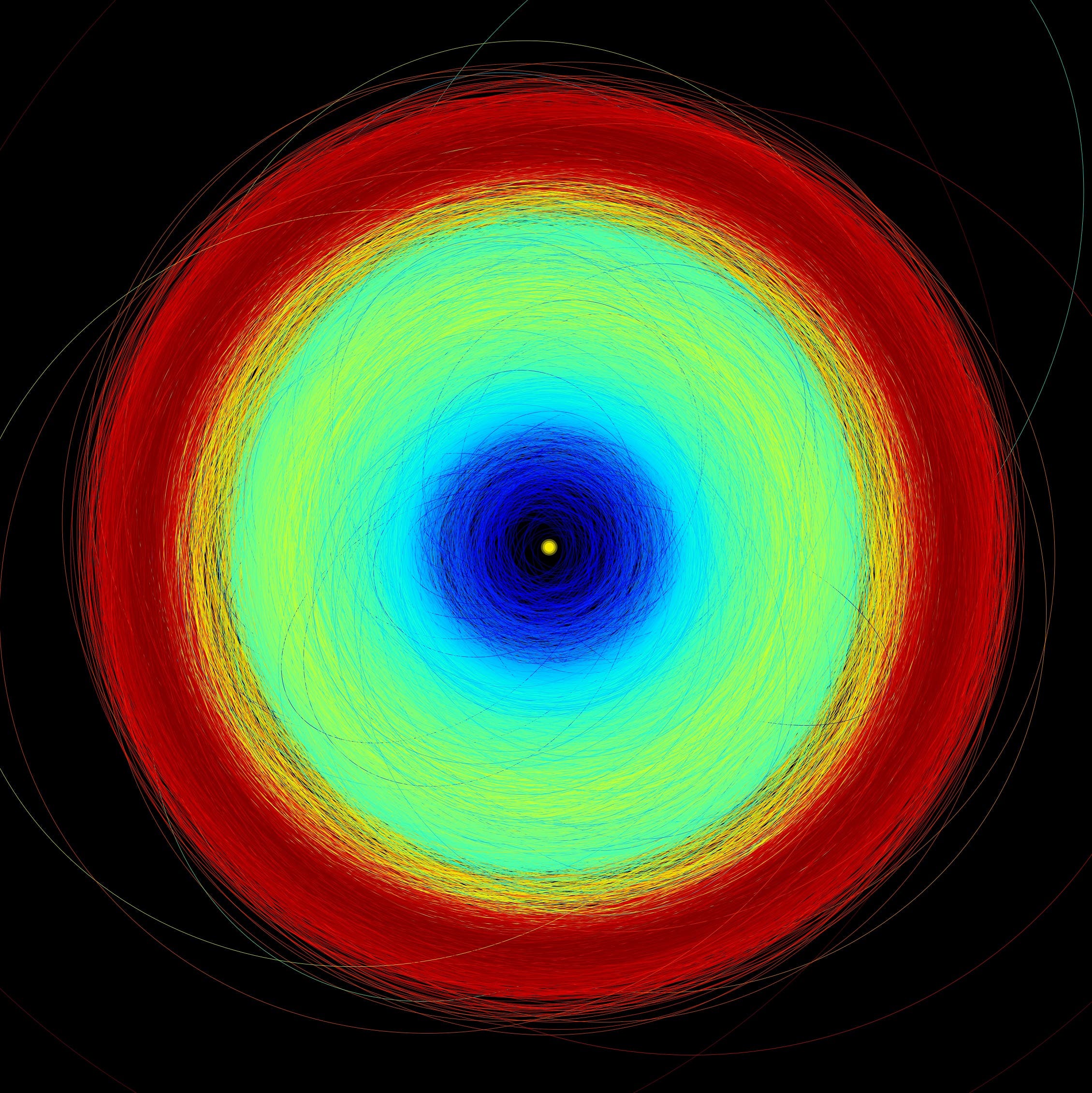
وجُهزت مهمة “غايا” بتلسكوبين وجهاز استشعار فوتوغرافي بدقة مليار بكسل، وهو يمسح جزءاً صغيراً جداً (بالكاد 1%) من النجوم في مجرتنا التي يبلغ قطرها 100 ألف سنة ضوئية، وحتى أبعد من ذلك.
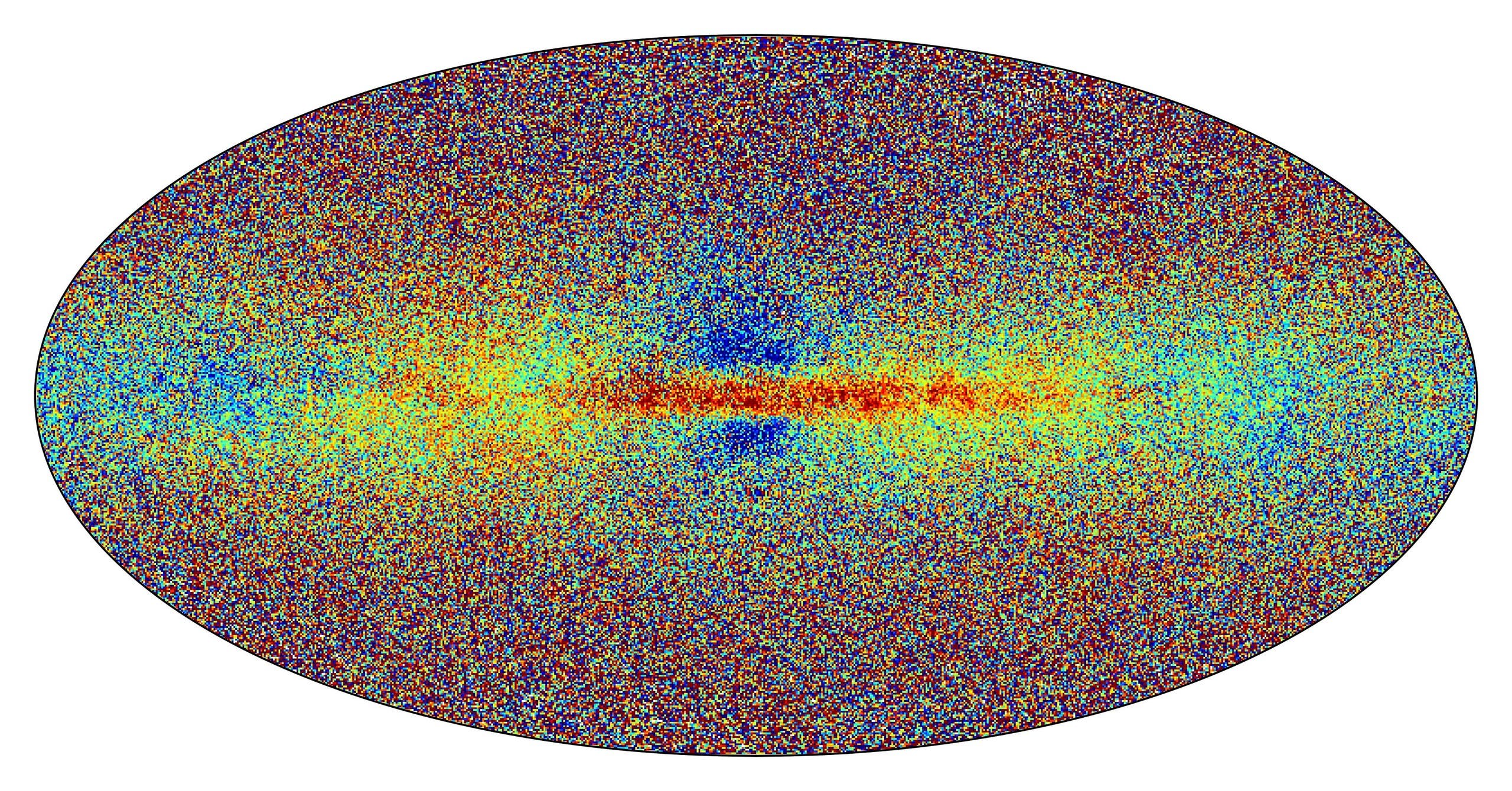
والأرقام التي تم الكشف عنها الاثنين مذهلة، فمن خلال تحليل البيانات المرسلة إلى الأرض والبالغ عددها 700 مليون يومياً، على مدى 34 شهراً، تمكّن “غايا” من توفير معلومات حول أكثر من 1.8 مليار نجم.
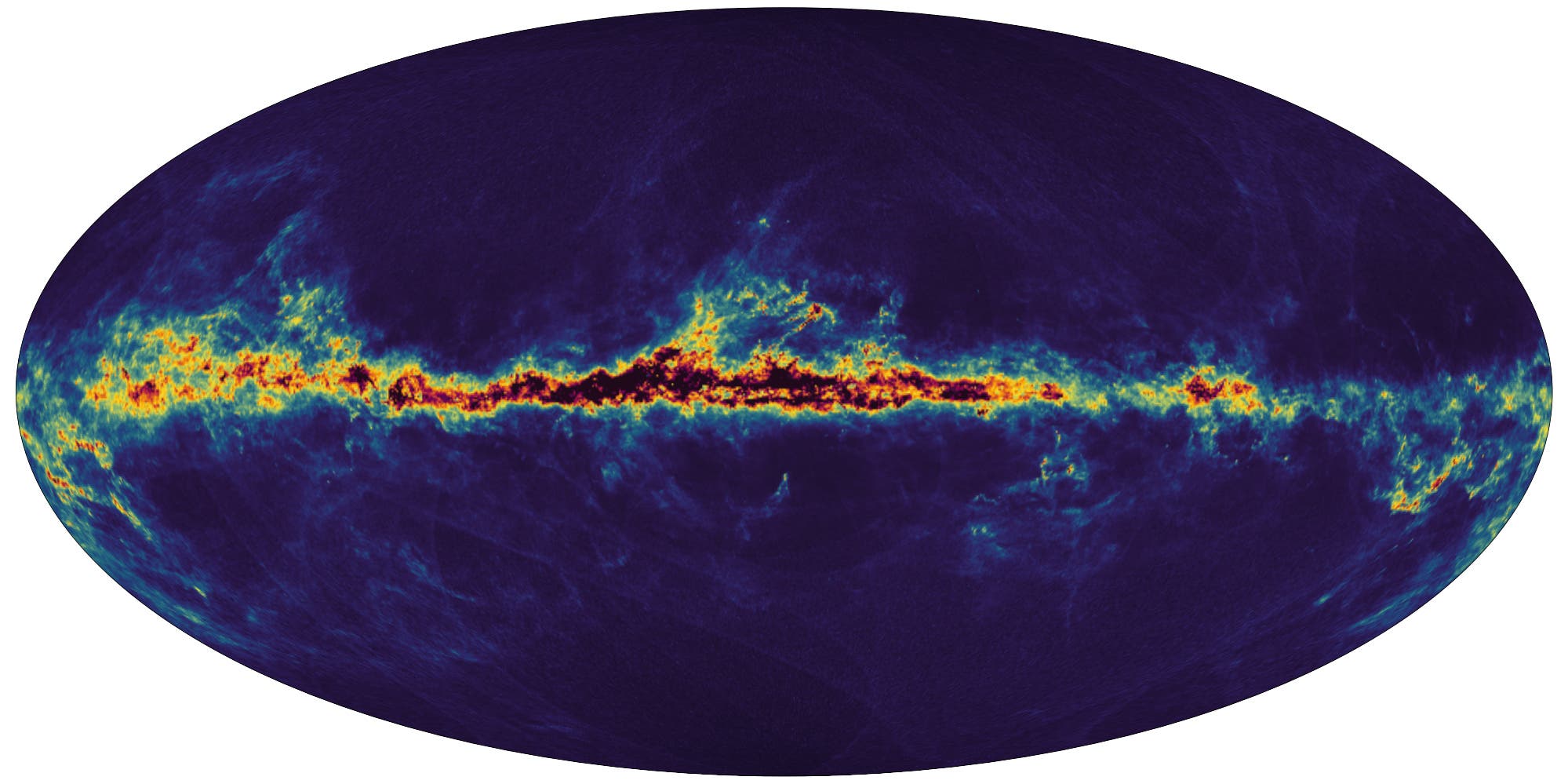
وتقدم المهمة مجموعة تفاصيل غير مسبوقة، بينها 220 مليون طيف قياس ضوئي، ما سيجعل من الممكن لأول مرة تقدير كتلة النجوم ولونها ودرجة حرارتها وعمرها. كما تقدم 2.5 مليون تركيبة كيمياوية جديدة، وهو “حمض نووي” يُعلمنا بمكان ولادة النجوم ورحلتها عبر المجرة.
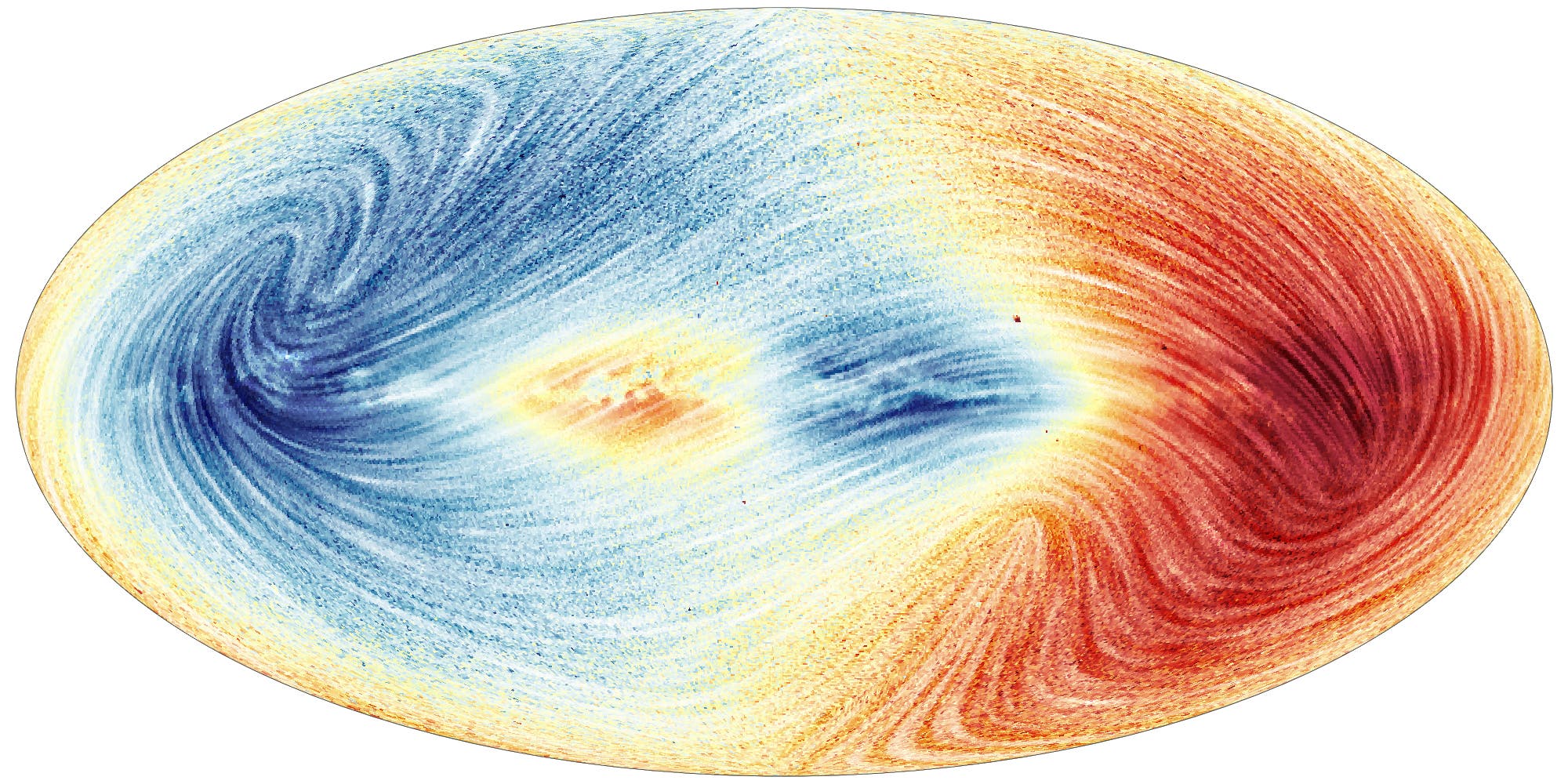
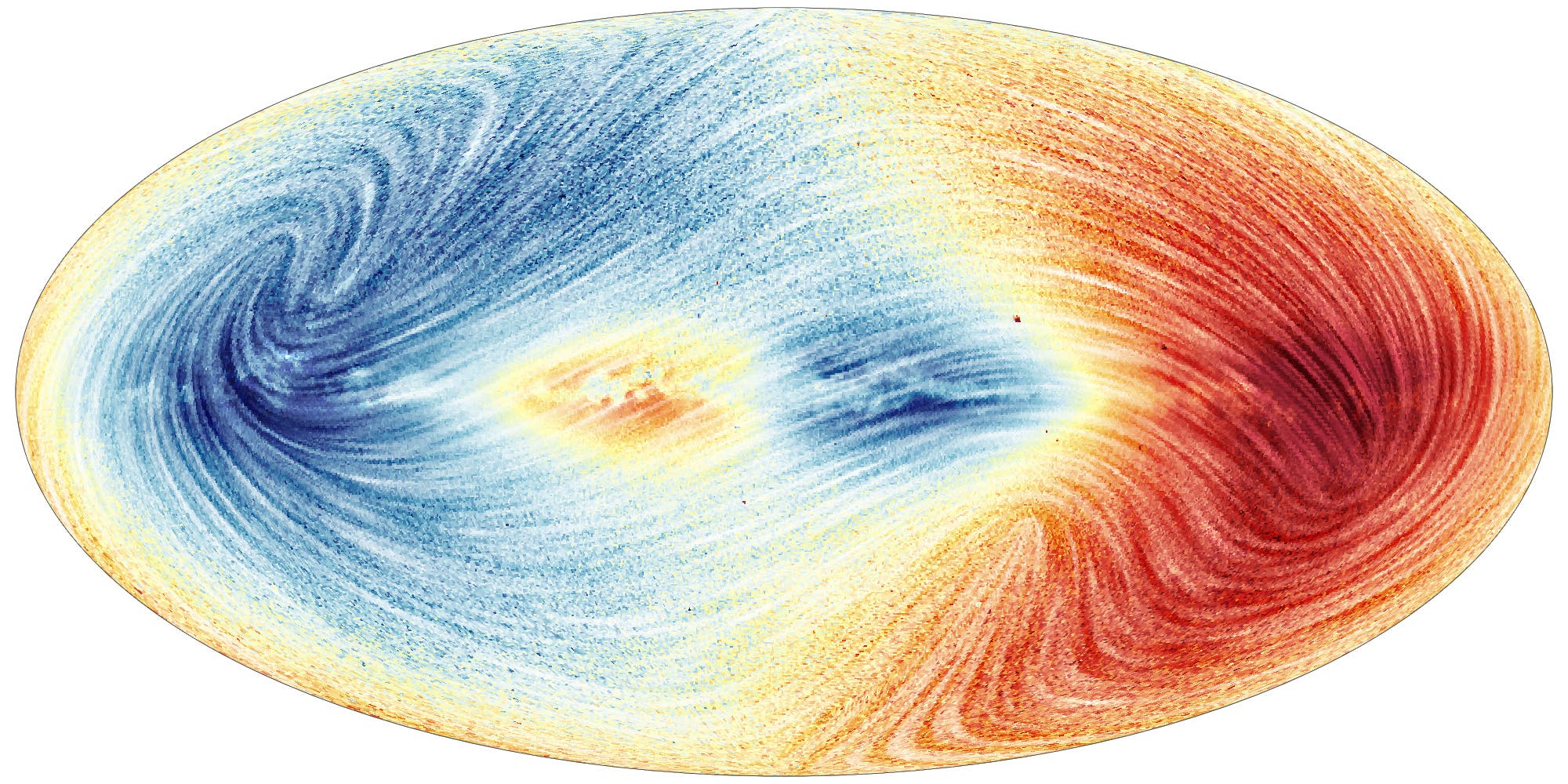
كما تقدم “غايا” بيانات عن 35 مليون سرعة شعاعية، تقيس تنقلها وتقدّم فهماً جديداً للتحركات في مجرة درب التبانة.
والمفاجأة الكبرى تتمثل في رصد “غايا” لأول مرة “هزات” نجمية، وهي حركات صغيرة على سطح نجم تغيّر شكله. هذا الاكتشاف يفتح “منجم ذهب لعلم النجوم على صعيد النجوم الضخمة”، لمعرفة طريقة عملها الداخلية، على ما أوضح كوني آيرتس من جامعة لوفان البلجيكية، العضو المتعاون في مهمة “غايا”.
من جهته، قال المدير العلمي لبعثة “غايا” في فرنسا فرنسوا مينيار إن هذه المهمة “تتخطى التوقعات على جميع المستويات”.
وقال لوكالة “فرانس برس” إن النتائج ترسم صورة مجرة “اكثر اضطراباً” مما كان متوقعاً. وأضاف: “اعتقدنا أنها وصلت إلى حالة من الثبات، منقلبة على نفسها برفق مثل سائل يتم تحريكه بهدوء بملعقة خشبية. ولكن الأمر ليس كذلك على الإطلاق! فحياتها مليئة بالحوادث والتحركات غير المتوقعة وليست بهذه البساطة”.
وعلى سبيل المثال، نظامنا الشمسي “لا يكتفي بالدوران في مستوى عمودي، فهو يرتفع وينخفض إلى أعلى وأسفل”، وفق فرنسوا مينيار.
كما أنه موطن لمجموعة غير متجانسة من النجوم، لم يكن بعضها موجوداً منذ البداية، وبعضها ربما تم “ابتلاعها” على طول الطريق من خلال التفاعلات مع مجرة القوس القزمة القريبة.
وفي هذا السياق قال أليخاندرا ريسيو بلانكو من مرصد كوت دازور: “مجرتنا هي بوتقة رائعة من النجوم”.
من جانبه، أوضح أنتوني براون رئيس كونسورسيوم “دي بي ايه سي” الدولي، الذي يشكّل سلسلة المعالجة الأرضية لسيل البيانات المرسلة من مهمة “غايا”، أن مستوى دقة هذه المهمة “سيسمح لنا بتتبع ماضي مجرة درب التبانة على مدى أكثر من 10 مليارات سنة”.
وللنجوم خاصية تتمثل في القدرة على العيش مليارات السنين، إذ يشير علماء الفلك إلى أن قياسها أشبه بأحفورة تخبرنا عن حالة المجرة أثناء تكوينها.
ومع سجل القياسات الثاني الذي تم تسليمه عام 2018، تمكن الباحثون من إظهار أن مجرتنا قد “اندمجت” مع أخرى قبل عشرة مليارات سنة.
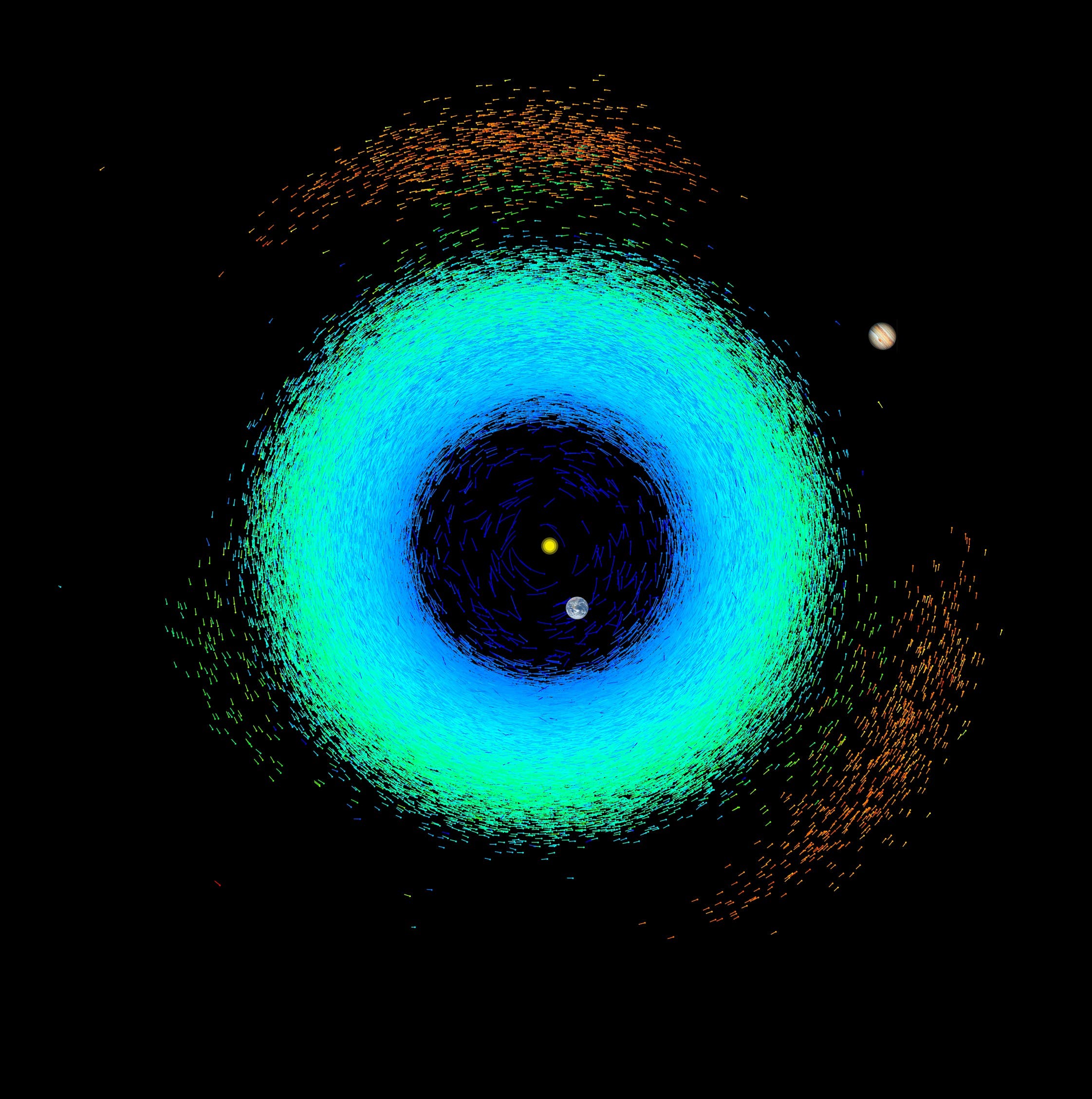
ويقدم السجل الجديد قياسات بدقة لا مثيل لها لـ156 ألف كويكب في نظامنا الشمسي، من خلال تفكيك تركيبة 60 ألفاً منها.
واستغرق الأمر خمس سنوات لتسليم هذا السجل الثالث للملاحظات الممتدة من 2014 إلى 2017.وسيتعين علينا الانتظار حتى عام 2030 للحصول على الإصدار النهائي، عندما تنتهي مهمة “غايا” من مسح الفضاء في عام 2025.
المصدر: وكالات





